▶ function.js 파일
export function getEmployees(callback) {
console.log('Sending request...');
const response = `[{ "id": 1, "name": "Jason", "email": "jason@codeitmall.kr", "department": "engineering" }, { "id": 2, "name": "Alice", "email": "alice@codeitmall.kr", "department": "engineering" }, { "id": 3, "name": "Brian", "email": "brian@codeitmall.kr", "department": "marketing" }, { "id": 4, "name": "Erica", "email": "erica@codeitmall.kr", "department": "marketing" }, { "id": 5, "name": "Wilson", "email": "wilson@codeitmall.kr", "department": "sales" }]`;
setTimeout(() => callback(response), 1000);
}
export function json(string, callback) {
console.log('Parsing string...');
const json = JSON.parse(string);
setTimeout(() => callback(json), 1000);
}
export function groupEmployees(employees, callback) {
console.log('Grouping employees...');
const res = {};
employees.forEach((employee) => {
const { name, department } = employee;
if (!(department in res)) {
res[department] = [];
}
res[department].push(name);
});
setTimeout(() => callback(res), 1000);
}https://seop-e.tistory.com/206
(4) Asynchronous JavaScript - Callback Hell
▶ function.js 파일더보기export function getEmployees(callback) { console.log('Sending request...'); const response = `[{ "id": 1, "name": "Jason", "email": "jason@codeitmall.kr", "department": "engineering" }, { "id": 2, "name": "Alice", "email": "a
seop-e.tistory.com
이 전 글에서 getEmployees 함수를 이용해서
웹 리퀘스트를 보내는 것을 흉내 냈었는데
실제로 웹 리퀘스트를 보낼 때는fetch() 함수를 많이 사용한다.
아래와 같이 코드를 작성해보면
// main.js
const response = fetch('https://naver.com');
console.log(response);다음과 같은 Promise pending 이라고 출력되는 것을 볼 수 있는데
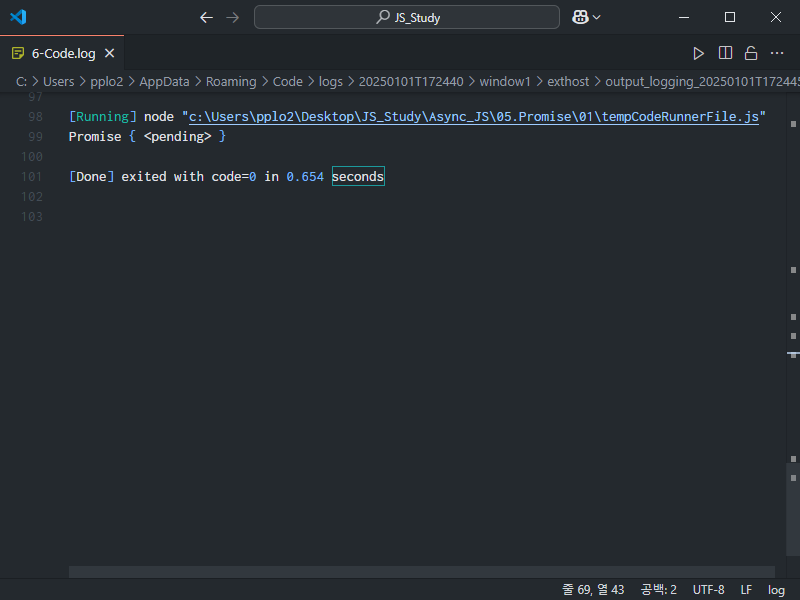
fetch 함수가 Promise라는 것을 리턴해서 그 값이 response에 저장된 것이다.
Promise에 대해 자세히 알아보자.
Promise
Promise는 비동기 작업이 완료되면 값을 알려주는 객체이다.
작업이 완료되면 값을 알려줄 것을 약속하기 때문에 이름이 Promise 인 것이다.
fetch는 오래 걸리는 작업이기 때문에 결과 값을 바로 돌려줄 수는 없으니까
일단 Promise를 돌려주고 나중에 작업이 완료되면
결과 값을 Promise에 채워 넣어주겠다는 개념이다.
이렇게 Promise를 바로 리턴하면 좀 더 직관적인 코드를 작성할 수 있다.
request를 보내고 response를 parsing해서 결과를 출력하는 코드를 아래와 같이 했다면
// main.js
import {getEmployees, json, groupEmployees} from './function.js'
getEmployees((response)=> {
json(response, (data) => {
console.log(data);
});
});
Promise 기반 fetch 코드를 완성하면 다음과 같다.
const response = await fetch('');
const data = await response.json();
console.log(data);여기서 await 문법이 나오는데 일단 잠시 대기.
Promise 기반 코드는 평소 익숙하게 코드가 한 줄 씩 쓰이고
이전 줄에서 선언한 변수를 다음 줄에서 사용하고 있다.
비동기 작업을 처리할 때도 익숙한 형태로 코드를 작성할 수 있다는 것이 큰 장점이고
자바스크립트에서 많은 비동기 코드가 Promise를 활용하는 이유이다.
'JS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| (7) Asynchronous JavaScript - 효율적인 비동기 코드 (0) | 2025.01.03 |
|---|---|
| (6) Asynchronous JavaScript - Promies 다루는 방법 (0) | 2025.01.02 |
| (1) ~ (4) Callback 정리 (0) | 2025.01.01 |
| (4) Asynchronous JavaScript - Callback Hell (0) | 2025.01.01 |
| (3) Asynchronous JavaScript - 비동기 함수들의 예시 (0) | 2024.12.31 |

